Apple has made their play: iPhone 6, iPhone6 Plus, Apple Pay and a wearable Apple Watch. Now that Apple Pay is here, how does this potentially affect retail transactions, e-commerce in general, and the projects in your pipeline.
We are at the cusp of the creation of a new ecosystem. But will Apple Pay fare better than Google Wallet did when it first launched in May 2011? There is a feeling of Déjà vu and Let’s Wait and See but also a sense of optimism and expectation of improved retail experience. In the near term iPhone 6 and iPhone6 Plus will be the real winners for Apple revenue, but in the long term Apple Pay will play an increasingly important role in generating revenue from previously untapped sources. As far as the role of Apple Watch itself is concerned, it’s revenue impact in the near term is uncertain but could become more significant as developers bring out apps and its role evolves.
Let us take a look at Apple Pay, as a prerequisite for starting to answer the myriad questions - Is this going to ignite mobile payments? Will it make digital payments more secure? How do the opportunities now stack up? How are the mobile operators likely to react? We all know Verizon, AT&T and T-Mobile were not cheer leaders for the Google Wallet. Softcard (rebranded from ISIS) is readying its own offer. What is PayPal thinking and how does this fit with the Braintree One-Tap announcements? How will Walmart react, and where does this fit with respect to MCX?
So why is this important?
The major factor for any new payment service is adoption. Offline retail payments have been sought to be addressed through a variety of methods from PayPal, Google and others, and so far by Apple using iBeacon functionality, BLE and other technologies. So far adoption of NFC has been a 10-year war between the banks and the mobile operators and has struggled to gain traction. It was important for the industry to know Apple’s position with respect to NFC as a standard for mobile payments.
We would all agree that in the current retail and e-commerce arenas one of the most pressing needs is security. The Apple announcement certainly seems to go a long way in addressing this need. For example the combination of its biometric sensors in its devices with the contactless transmission of one-time card number combined with the fact that Apple creates a device-only account number that they store in the secure element, provides a basic foundation for enhanced security. Furthermore as far as customer perspective is concerned, the fact that one can find the phone more easily and take action if it is lost goes a long way towards addressing concerns.
Back in 2011 we had the entry of the Google wallet, and each of the card schemes announced their own wallets as well. Still consumers and merchants failed to adopt. While contactless cards gradually crept into use, paying at retail POS by phone continued to prove elusive, for a variety of reasons. For the longest time, one of the main reasons was claimed to be lack of handsets. However, customer security concerns and more importantly business model were arguably even greater challenges.
And what about adoption?
One of the major challenges in creating a successful service is the ability to bring a large customer base on board rapidly. At the retail level this translates to satisfying consumers both on convenience and trust. In this respect Apple has 800 million customers from their iTune stores as ‘card on file’. However there is a separate step involved to get consumers to start to use Apple Pay for contactless payments as it launches shortly in the US.
This is where the convenience and trust come into play and is something for which we’ll need to wait and watch.
Additionally the Apple API will be available to developers and this is an exciting space to watch. We saw how millions of apps became available for the iPad and iPhone – now Apple Watch is here, and although tethered to the iPhones for the present, it presents a new frontier of innovation. For the present the watch offers an opportunity to integrate a variety of health and fitness related services – something I think we will hear a lot more about shortly.
Merchant support has already been announced: McDonalds, Integration with Uber, a food app from Panera, Major League Baseball's app to order tickets from your phone, and Open Table to pay your bill from your iPhone 6 or iPhone 6 Plus. Apple API is to be offered in iOS 8 to allow app developers to integrate Apple Pay into their applications.
So how will mobile operators react?
Apple has a following, and is not overly dependent on mobile operators to push their phones, however operator subsidies that could be as high as $500 considerably help make them affordable. The rapid adoption of smartphones across the world has changed the balance of power. Certainly in the US, Apple is Top Dog as a smartphone manufacturer, with 42.1% OEM market share as of June 2014 according to comScore reports.
Some news is in already as to how mobile operators view this. Softcard (formerly ISIS) have made a statement that they see Apple’s support to NFC as a significant step that sets the stage for rapid scale adoption of mobile commerce.
However while in the US and Europe Samsung and Apple dominate, the share of both providers has been dropping in emerging markets where we see an emerging fragmentation. In urban China, Xiaomi with its affordable RedMi model continues to go from strength to strength, securing a 27% share of smartphone sales in the important China market in the second quarter of 2014, compared with 21.1% for Samsung. And payments by watch + iPhone cannot be a top priority for the masses in emerging markets, although urban, higher income Chinese consumers do seem to be quite interested.
What about the others?
As we describe in great detail in our book, payments has become a hotly contested space. Another fairly late entrant is Amazon. Just take a look at the Amazon Fire Phone, the first smartphone designed by Amazon. Amazon has vowed to create a whole new shopping experience and until December 31, 2014 the fire phone comes with 800 Amazon Coins to spend on apps, games and more as well as 10% discounted purchase for more Coins. They also offer other benefits including a year of Prime Benefits (Video, Delivery, Books and more).
Such bundles of value are what the customer is increasingly coming to expect, and the whole Apple offer will need to evolve to meet the competition.
Too little, too late?
Without doubt, Apple is a late starter where contactless payments are concerned. Like a swan, the movement seemed to be more ‘under-water’, as news of patents obtained for motion based payments got out back in January 2013. For instance, Apple obtained a US Patent for a digital wallet and virtual currency. It described a system of managing credits via a mobile device. Mobile users would be able to receive credits or coupons stored in their accounts. Check out Patently Apple for the background on Apple patents for payments.
Yet, little happened until now.
-
Back in June 2013 Apple released its first mobile commerce platform, called the iCloud Keychain: consumers could store passwords and financial details for use across several Apple devices and they could log into websites or make purchases online. But the platform did not support NFC and existed as an application rather than a physical device.
-
Earlier in June 2012, the Apple bar-code-based Passbook mobile wallet was launched, as a basic mobile wallet without payment functions, using barcodes to store and represent multiple boarding passes, store cards, and movie tickets. It had location-enabled alerts, and real-time updates and it displayed passes based on a specific time or location. When consumers walk into a participating shop the loyalty card appears and can be scanned to pay or check balance. It was expected that this could evolve into a mobile payment service by linking the Passbook to customer credit cards and iTunes accounts.
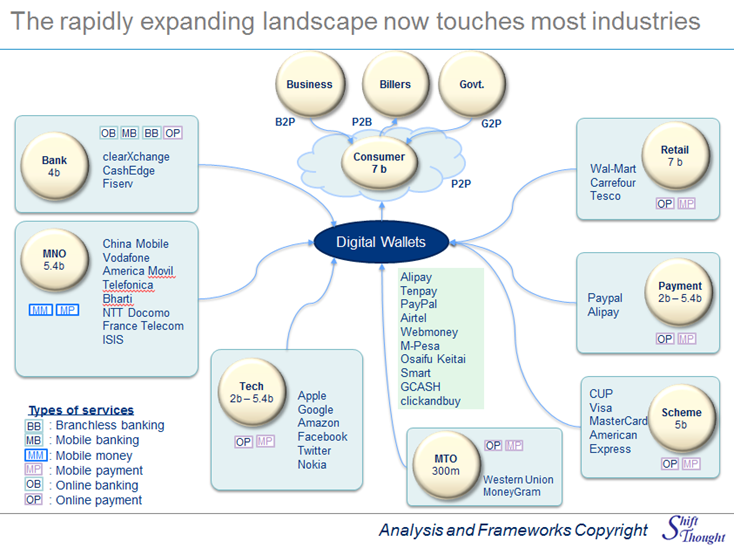
Effect of Apple Play on the Digital Money Game
The contactless payments that Apple Pay now propose to offer come as a reinforcement to the Digital Money Game of some players, but a threat to others.
And it is no longer enough to offer just mobile payments. To gain adoption, Apple must be able to offer a range of ways to pay, across the web and other channels including TV, now being hotly talked about in emerging markets. And they must get the interoperability story right, and rapidly prove the concept beyond the US market.
Read all about this, and work out your own strategy with our recently published, highly acclaimed book, The Digital Money Game. Also, if you would like to discuss immediate ramifications on your projects just drop me a line at coak@shiftthought.com.





![clip_image002[4] clip_image002[4]](http://digitalmoney.shiftthought.com/files/2014/09/clip_image0024.jpg)
![clip_image004[4] clip_image004[4]](http://digitalmoney.shiftthought.com/files/2014/09/clip_image0044.png)